
Check Me Out!
 Forget GCSEs, A Levels and Degrees, your baby will be expected to take her very first test a couple of minutes after birth. Find out what those new baby checks are for and what they mean.
Forget GCSEs, A Levels and Degrees, your baby will be expected to take her very first test a couple of minutes after birth. Find out what those new baby checks are for and what they mean.
The First Few Minutes
The first test, the Apgar, is taken at one and five minutes after birth. Designed by doctor Virginia Apgar in 1952, it’s an easy way for doctors to assess your baby’s health. It looks at Appearance, Pulse, Grimace, Activity and Respiration and your baby can score a maximum of ten points. For example, appearance looks at skin colour to rule out circulation problems. The scores don’t usually mean long-term problems and by five minutes, most babies get a score of nine.
One Hour
Once you have had a cuddle with your newborn, your midwife will weigh her, measure her head circumference and check her temperature. This will be recorded in her child health record, which you’ll take to all future check-ups.
Within 72 Hours Of The Birth
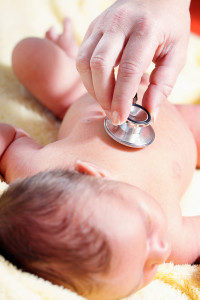 The next thing is a complete check-up, performed by a Paediatrician or a midwife with specialist training.
The next thing is a complete check-up, performed by a Paediatrician or a midwife with specialist training.
Head
A squashed and misshapen head is common in a newborn; the bones haven’t fused, allowing it to squeeze through the birth canal. If baby was born using forceps, there may be bruises but they will soon clear up.
Eyes
Your doctor will shine a light to check for a red reflex and may also perform a simple hearing test.
Reflex
The doctor pops his finger into baby’s mouth to check the suckling reflex is strong and to rule out cleft palate or tongue-tie. Both of these can interfere with breastfeeding.
Heart
This is checked with a stethoscope. Some difficulties are common in the early days and soon right themselves without treatment.
Lungs. They are checked to make sure they are clear of fluid and there’s good air flow into both lungs.
Genitals
They are examined for abnormalities. Your baby was exposed to your hormones in the womb, so genitals may be swollen and dark and baby may have swollen breasts – even if it’s a boy! A girl may have a little discharge from the vagina for a few weeks. Boys are checked for undescended testicals and that the penis is properly formed. The anus is also checked.
Skin
They look for birthmarks and blemishes; some of these don’t appear immediately and disappear later.
Fingers and toes
These are counted and webbing checked. Palms should have two creases– a single one can be associated with Down’s Syndrome.
Feet are checked for talipes or club foot.
Spine
Assessed for straightness and to rule out spinabifida, when the spinal cord is not properly formed. A deep dimple at the spine’s base may mean problems such as incontinence and weakness.
Hips
They are moved gently to check that joints are working well. If they are ‘clicky’ or not well formed, treatment may be necessary.
Reflexes
The doctor will assess rooting, grasping and sucking and the Moro or ‘startling’ reflex.
First Blood Test
 Five to eight days after the birth,your midwife will take a tiny amount of blood from a heel prick. This checks
Five to eight days after the birth,your midwife will take a tiny amount of blood from a heel prick. This checks
- Phenylketonuria (PKU), an enzyme deficiency
- A problem with the lungs and digestive system called Cystic fibrosis.
- A condition called MCADD which affects conversion of fat to energy (rare).
- The blood disorder, sickle cell disease.
- A deficiency in thyroid production.
- Rare metabolic disorder Homocystinuria.
- The conditions Maple syrup urine disease, isovaleric acidaemia and glutaric aciduria type 1, problems where the body can’t process proteins.
All the physical checks are repeated at various stages later on but if you have any questions or concerns, talk to your midwife or doctor.
